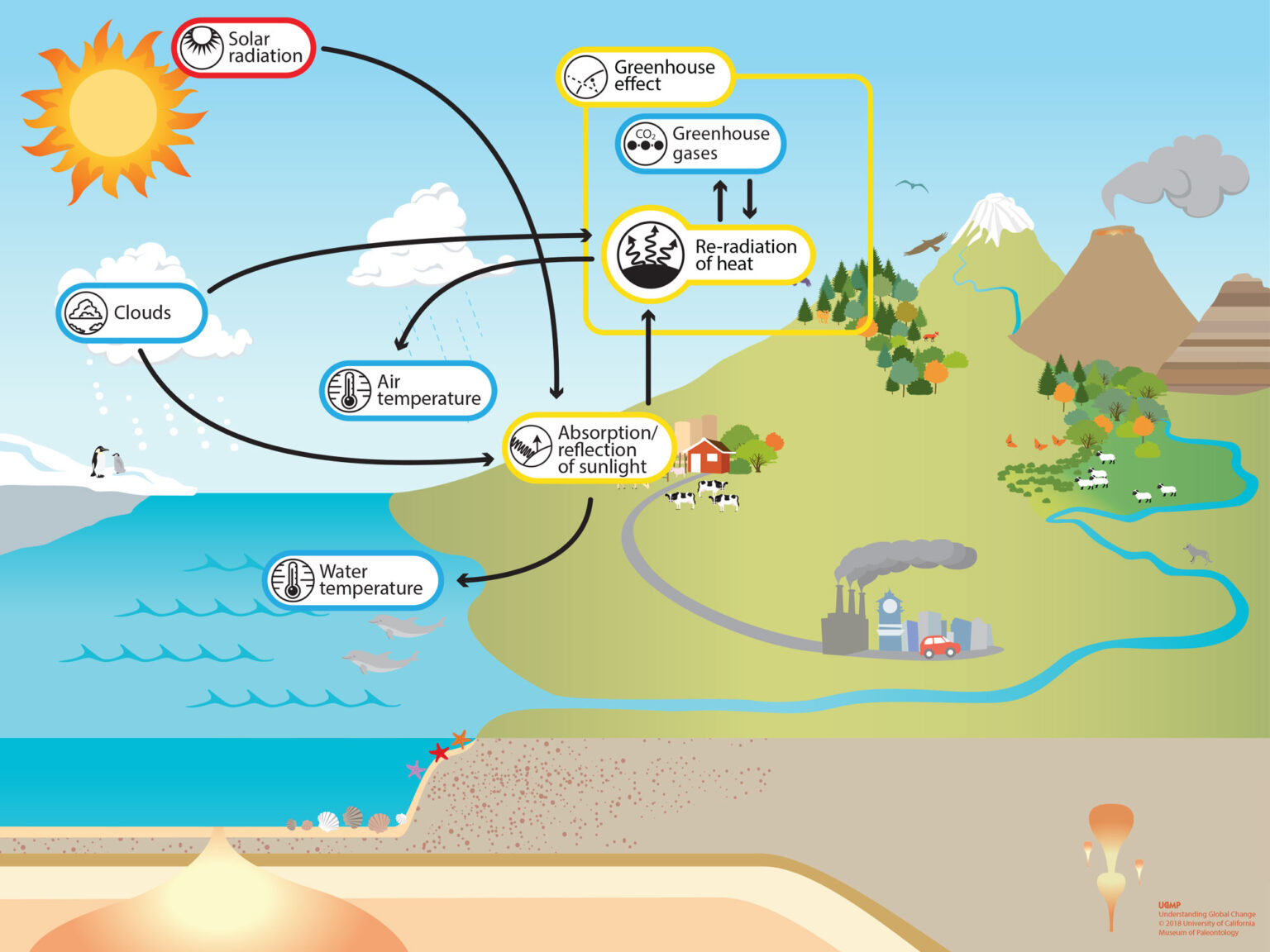
Climate change has been altering global weather patterns, causing extreme heat waves and unpredictable temperature shifts. As these changes intensify, they are fundamentally reshaping the world’s Energy Demands. Understanding the relationship between climate change, extreme heat, and energy usage is critical to ensuring a sustainable and resilient energy future.
The Growing Frequency of Heat Waves
In recent years, heat waves have become more frequent and intense due to the effects of climate change. Regions that once experienced moderate summers are now enduring prolonged periods of extreme temperatures. This increase in global temperatures is pushing power grids to their limits as energy consumption spikes to meet the rising demand for air conditioning and cooling systems. According to studies, the energy demand for cooling alone could rise by as much as 50% by 2050.
Energy Demand Surges with Heat
One of the most immediate impacts of extreme heat is the increase in electricity consumption. Air conditioners and cooling devices are major contributors to energy use, especially during peak hours. As more homes, businesses, and industries rely on cooling systems to combat the heat, energy providers struggle to keep up with the increased load. In some cases, this has resulted in blackouts and power outages, especially in areas with aging infrastructure that cannot handle the demand.
Shifts in Peak Energy Usage
Traditionally, peak energy consumption has occurred in the winter months when heating needs were at their highest. However, with the onset of more extreme heat, peak energy usage is shifting to the summer months. This shift forces energy companies to rethink their strategies, including upgrading infrastructure, enhancing grid resilience, and diversifying energy sources to handle higher summer demands.
Renewable Energy Under Pressure
While renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power offer solutions to increasing energy demands, they too are being impacted by climate change. Prolonged heat waves can reduce the efficiency of solar panels and wind turbines. Extreme heat can also cause droughts, affecting hydroelectric power plants, which rely on water flow to generate electricity. The challenge is not only meeting energy demands but also ensuring that renewable sources can adapt to these changing conditions.
The Role of Energy-Efficient Appliances
Energy efficiency plays a key role in mitigating the strain on power grids during heat waves. The demand for energy-efficient appliances, such as air conditioners and fans, has grown as consumers look for ways to reduce their energy consumption. Governments and energy providers are also offering incentives for the adoption of energy-efficient products to help reduce the overall burden on power systems during extreme temperatures.
Adapting to the New Normal
The growing energy demands driven by climate change and extreme heat are forcing societies to rethink how they consume and produce energy. Energy providers must invest in grid resilience, renewable energy storage technologies, and energy-efficient solutions. Governments are also stepping in with policies that encourage energy conservation, support for renewable energy projects, and the development of smart grids that can better manage fluctuating energy demands.
Conclusion
As climate change drives more extreme heat events, the reshaping of global energy demands is inevitable. Balancing the need for reliable energy with environmental sustainability is a complex challenge. By embracing renewable energy, enhancing grid infrastructure, and promoting energy-efficient practices, societies can better adapt to the new energy landscape shaped by climate change. The time to act is now, before the impacts of extreme heat become even more pronounced.