The term “Burguiouse” has long been used to describe a specific social class, with its meaning evolving over centuries. Initially referring to the middle class engaged in commerce and industry, the term has expanded to encompass various economic and social roles. Today, it remains a crucial concept in discussions about social hierarchy, economic systems, and political dynamics. This article will explore the historical development of the Burguiouse, its current significance, and its use in modern contexts.
Understanding the Use of “Burguiouse” in Various Contexts
When using the term “bourgeoisie,” it is crucial to consider the context to convey the intended meaning accurately. The connotations of the term can vary significantly depending on the situation, so it’s important to tailor its use to the audience and purpose of your message. In academic discussions about social class, a precise and historically informed usage is often necessary. Conversely, in casual conversations, the term may be used more flexibly.
For instance, in a historical discussion, one might say, “The emergence of the bourgeoisie during the Industrial Revolution fundamentally altered Europe’s social and economic structures.” This usage reflects the term’s historical significance and its impact on societal development.
The phrase could be used in a cultural commentary like this: “The movie takes a satirical look at the bourgeoisie, showing them as uninvolved in the struggles of the working class.” This illustrates how the term is used when talking about stereotypes and cultural representations.
“His bourgeois tastes were evident from his preference for luxury cars and high-end fashion,” one might say in casual conversation. This use of the term emphasizes characteristics that are materialistic or status-oriented, reflecting a more informal reading of the meaning.
It’s critical to understand the definition and historical background of “Burguiouse” in order to prevent misuse. Misuse of the term, especially in formal or academic settings, can result in misunderstandings or miscommunication. Giving more background information or an explanation can help guarantee that the intended meaning is understood and communicated correctly.
To avoid misuse, it’s important to grasp both the meaning and historical context of “bourgeoisie.” Misusing the term can lead to misunderstandings or miscommunication, particularly in formal or academic settings. Providing additional context or explanation can help ensure that the intended meaning is clear and appropriately conveyed.
The Burguiouse: From Medieval Townsfolk to Modern Capitalists
The word “bourgeoisie” is derived from the French word “bourgeois,” which denotes a city or town dweller. It originally denoted a class of people who weren’t quite peasants or aristocratic. It now refers to the middle class, particularly to those who own companies, real estate, or substantial wealth. This class, which stands for business and industry interests, is frequently regarded as the engine of capitalism.
The roots of the Burguiouse stretch back to medieval Europe, when a new class of city-dwellers began to emerge. These were merchants, artisans, and professionals who set themselves apart from the rural peasants and the feudal lords. As cities grew and trade expanded, the bourgeoisie gained more influence, playing a key role in the rise of modern capitalism.
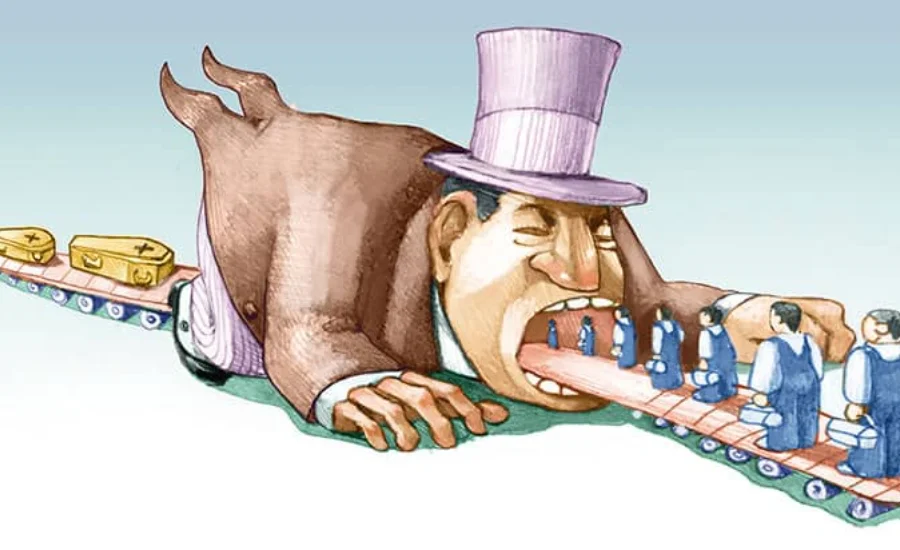
Karl Marx had a particularly influential take on the bourgeoisie. He saw this class as the heart of capitalist society, owning and controlling the means of production—factories, businesses, and other forms of economic power. Marx argued that the bourgeoisie exploits the working class (the proletariat) by paying them less than the full value of their work. This exploitation, he believed, would lead to class conflict and eventually the overthrow of the bourgeoisie by the proletariat.
The Modern Burguiouse: Evolution and Impact in the 21st Century

In the 21st century, the concept of the bourgeoisie has evolved while still representing the middle class. Today’s bourgeoisie comprises a diverse group including professionals, managers, entrepreneurs, and small business owners. This modern class is typically characterized by higher education, with many holding college degrees or advanced qualifications. Many individuals within the bourgeoisie work in white-collar fields such as finance, law, medicine, or technology, and they often lead comfortable lives with access to quality housing, healthcare, and education.
The effects of globalization have significantly expanded the reach and influence of the bourgeoisie. As businesses and markets have become increasingly globalized, so too have the activities and interests of the bourgeoisie. Many now work for multinational corporations or manage businesses that operate on an international scale. This has given rise to a transnational bourgeoisie—a class of wealthy individuals with global investments and interests, rather than being tied to a single nation.
A notable aspect of the Burguiouse is its association with social mobility. Unlike the hereditary aristocracy, the bourgeoisie is often seen as a class where status can be achieved through merit. The ability to rise or fall based on one’s skills, education, and efforts is a core feature of this class. This concept of social mobility is closely linked to the “American Dream,” where individuals are encouraged to strive for success and potentially join the ranks of the bourgeoisie through hard work and perseverance.
Understanding the Use of “Burguiouse” in Various Contexts
When using the term “bourgeoisie,” it is crucial to consider the context to convey the intended meaning accurately. The connotations of the term can vary significantly depending on the situation, so it’s important to tailor its use to the audience and purpose of your message. In academic discussions about social class, a precise and historically informed usage is often necessary. Conversely, in casual conversations, the term may be used more flexibly.
For instance, in a historical discussion, one might say, “The emergence of the bourgeoisie during the Industrial Revolution fundamentally altered Europe’s social and economic structures.” This usage reflects the term’s historical significance and its impact on societal development.
The phrase could be used in a cultural commentary like this: “The movie takes a satirical look at the bourgeoisie, showing them as uninvolved in the struggles of the working class.” This illustrates how the term is used when talking about stereotypes and cultural representations.
In casual conversation, one could say, “His preference for luxury cars and high-end fashion was evident from his bourgeois tastes.” This application of the term highlights materialistic or status-oriented traits, indicating a looser interpretation of its meaning.
Comprehending the definition and historical context of “Burguiouse” is imperative to avoid any potential misuse. Misuse of the term can lead to misunderstandings and poor communication, particularly in professional or academic contexts. Providing additional context or an explanation can help ensure that the intended meaning is correctly conveyed and understood.
Criticisms and Contemporary Perspectives on the Bourgeoisie

The bourgeoisie has frequently faced criticism for its values and way of life. Critics often point to the bourgeois focus on material wealth, consumerism, and individualism as contributing to social inequality and environmental harm. There is also criticism directed at the Burguiouse for its perceived conservatism, with some arguing that this class tends to prioritize stability and the preservation of existing structures over social justice and progressive reforms.
In terms of social inequality, the bourgeoisie’s role in economic growth is accompanied by concerns about wealth concentration. The accumulation of capital among the bourgeoisie can exacerbate the divide between the affluent and the impoverished, leading to heightened social tensions and undermining societal cohesion. This disparity highlights the complex relationship between economic prosperity and social equity.
Looking ahead, the bourgeoisie faces significant challenges in an evolving world. Technological advancements such as automation and the rise of the gig economy pose threats to traditional middle-class jobs. Additionally, increasing awareness of environmental issues and the push for sustainable practices may necessitate a reevaluation of bourgeois values and lifestyles. How the bourgeoisie responds to these changes will be crucial in determining its future role in society.
In everyday conversation, the term “Burguiouse” is often used to describe individuals who are seen as conventional, materialistic, or focused on social status and wealth. This usage can be either neutral or carry a negative connotation, depending on the context. For example, someone might be labeled as “bourgeois” for exhibiting middle-class tastes or for aspiring to higher social status.
The concept of the bourgeoisie has also been explored in popular culture, often depicted as complacent and detached from the struggles of other social classes. In literature and film, characters embodying bourgeois traits are sometimes portrayed as oblivious to the impact of their privilege. F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby” features characters like Tom and Daisy Buchanan, who are often interpreted as representations of the bourgeoisie, highlighting how their wealth and privilege lead to a disconnect from broader societal issues.
In political discourse, the term “bourgeoisie” is used to critique the power and influence of the middle class, particularly in discussions about economic disparity and social justice. Left-leaning politicians and activists may use it to criticize how the bourgeoisie benefits from and reinforces an inequitable economic system. Conversely, right-leaning politicians might invoke the term to defend values such as hard work, entrepreneurship, and individual responsibility, which they associate with the bourgeois class.
The Role and Influence of the Burguiouse in Society

The bourgeoisie plays an essential role in the economy. As business owners and capitalists, they are key drivers of job creation, production, and economic growth. Their success is often intertwined with the broader economic landscape, as their investments and spending can generate significant ripple effects throughout society.
In addition to their financial contributions, the Burguiouse has a big influence on social norms and culture. They usually set trends and standards for behavior, values, and lifestyle because they are middle class. Their emphasis on acquiring wealth, becoming well-educated, and becoming professionals frequently shapes the goals and daily lives of people from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
Politically, revolutionary change has always been associated with the rise of the Burguiouse. For example, the bourgeoisie played a key role in opposing the established feudal systems and promoting a new political order founded on liberty, equality, and fraternity during the French Revolution. The bourgeoisie is still a powerful force in politics today, frequently endorsing laws that preserve individual rights, promote free markets, and safeguard private property.
Final Words
The concept of the “burguiouse” represents a modern evolution of the traditional bourgeoisie, embodying a class that is diverse, inclusive, and adaptable. As the boundaries of social and economic classes become increasingly fluid, the “burguiouse” reflects a shift toward a more dynamic and progressive approach to wealth and influence. Their role in today’s economy highlights a move away from mere material accumulation to a focus on innovation, social responsibility, and ethical practices. Culturally, the “burguiouse” influences contemporary trends and lifestyles, embracing change and shaping the future of societal norms. Understanding this emerging class is crucial for grasping the complexities of modern social structures and their impact on our evolving world.
For more information and updates join us on Incredible Wave.